
No content returned. Gemini error: Resource exhausted. Please try again later. Please refer to https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/error-code-429 for more details.


No content returned. Gemini error: Resource exhausted. Please try again later. Please refer to https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/error-code-429 for more details.


Demystifying Intraday Trading: Learn the basics, strategies, risks, and rewards of day trading in the Indian stock market. Navigate NSE/BSE like a pro! Intrada
Demystifying intraday trading: Learn the basics, strategies, risks, and rewards of day trading in the Indian stock market. Navigate NSE/BSE like a pro!
The Indian stock market offers various avenues for investors, ranging from long-term investments to shorter-term speculative plays. One such approach, often attracting both seasoned traders and curious newcomers, is intraday trading. But what exactly is it, and how does it work within the context of the Indian financial landscape?
In essence, intraday trading, also known as day trading, involves buying and selling stocks (or other financial instruments) within the same trading day. The goal is to profit from short-term price fluctuations, closing out all positions before the market closes. This means no stocks are held overnight, eliminating overnight risk associated with market-moving news or events.
The Indian stock market, primarily represented by the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), provides the platform for this activity. Trading hours typically run from 9:15 AM to 3:30 PM IST, offering a limited window for executing these trades.
Unlike long-term investments where the fundamental strength of a company plays a crucial role, intraday traders focus heavily on technical analysis, charting patterns, and market sentiment. News events, earnings announcements, and even global market trends can significantly impact stock prices within a single day, creating opportunities (and risks) for intraday traders.
It’s crucial to distinguish intraday trading from other common investment approaches:
The risk profile of intraday trading is significantly higher than these longer-term strategies. While the potential for quick profits exists, the risk of substantial losses is also considerable. Unlike long-term investments, where time can mitigate short-term volatility, intraday traders must make quick decisions in a fast-paced environment.
Successful intraday trading requires a combination of knowledge, discipline, and the right tools. Here’s a breakdown of essential elements:
Technical analysis is the backbone of intraday trading. It involves studying historical price charts and using various indicators to predict future price movements. Some commonly used technical indicators in the Indian context include:
Risk management is paramount in intraday trading. Given the inherent volatility, it’s crucial to implement strategies to protect your capital. Key risk management techniques include:
Selecting the right stocks for intraday trading is crucial. Focus on stocks that are liquid (easily bought and sold) and exhibit sufficient volatility to create trading opportunities. Look for stocks listed on the NSE or BSE with high trading volumes.
Avoid illiquid stocks, as you may struggle to enter or exit positions at your desired price. Also, avoid extremely volatile stocks that can lead to unpredictable and potentially devastating losses.
Keep abreast of market news, economic events, and company-specific announcements that could impact stock prices. Regularly monitor financial news websites, business channels, and research reports.
Understanding the market sentiment and identifying potential catalysts for price movements can provide a significant edge in intraday trading.
Select a reliable and user-friendly trading platform that provides real-time market data, charting tools, and efficient order execution. Consider factors such as brokerage fees, margin requirements, and customer support.
Several reputable brokerage firms in India offer specialized platforms for intraday traders. Research and compare different options to find the one that best suits your needs.
While the allure of quick profits can be tempting, it’s essential to be aware of the significant risks associated with intraday trading:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates the Indian stock market and sets guidelines for intraday trading. These guidelines aim to protect investors and ensure fair market practices.
Some key SEBI regulations relevant to intraday trading include:
It’s crucial for intraday traders to understand and comply with all applicable SEBI regulations to avoid penalties and ensure ethical trading practices.
Before venturing into intraday trading, carefully assess your risk tolerance, financial resources, and time commitment. It’s not a get-rich-quick scheme and requires significant effort and discipline.
Consider the following questions:
If you answer “no” to any of these questions, intraday trading may not be suitable for you. Consider exploring other investment options that align better with your risk profile and financial goals.
For those seeking less risky and time-consuming investment strategies, several alternatives are available in the Indian market:
These alternatives offer a more balanced approach to investing, allowing you to build wealth over time without the high risks and demands of intraday trading. Remember to consult with a financial advisor to determine the best investment strategy for your individual needs and circumstances. Understanding the nuances of the Indian equity markets is crucial, whether you’re involved in active trading or long-term investment strategies.


Unlock profit potential with the best technical analysis tools in trading apps! Master charts, indicators, & patterns for smart Indian stock market investments.
Unlock profit potential with the best technical analysis tools in trading apps! Master charts, indicators, & patterns for smart Indian stock market investments. Start today!
The Indian stock market, with its vibrant exchanges like the NSE (National Stock Exchange) and BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange), offers a plethora of opportunities for investors. However, successful trading requires more than just intuition; it demands a disciplined approach based on solid analysis. Technical analysis, the art of predicting future price movements based on historical data, plays a crucial role in informed decision-making. For Indian investors, especially those using trading apps, mastering technical analysis tools can significantly enhance their trading performance.
Gone are the days of relying solely on broker recommendations. Today’s trading apps empower individuals with real-time data, interactive charts, and a comprehensive suite of technical indicators, all at their fingertips. This article explores the essential technical analysis tools available in trading apps that can help you navigate the Indian equity markets and make profitable investment choices, whether you’re trading equities, derivatives, or even exploring options.
Before diving into specific tools, let’s understand why technical analysis is vital for Indian investors:
For Indian investors, especially those participating in Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs) in equity mutual funds or holding long-term investments in instruments like PPF (Public Provident Fund) and NPS (National Pension System), understanding market trends through technical analysis can inform decisions about rebalancing portfolios or adjusting investment strategies based on market outlook.
Here’s a breakdown of the most useful technical analysis tools readily available in modern trading apps:
Trading apps offer various chart types to visualize price data, each providing a unique perspective:
Candlestick charts are widely favored by technical analysts due to their ability to visually represent market sentiment and potential turning points. Understanding candlestick patterns like “Doji,” “Hammer,” and “Engulfing” can provide valuable insights into market dynamics.
Trendlines are lines drawn on charts to connect a series of high points (in a downtrend) or low points (in an uptrend). They help identify the direction of the prevailing trend. Breaking a trendline can signal a potential trend reversal.
Drawing accurate trendlines is crucial. Connecting at least two significant highs or lows is generally recommended to establish a valid trendline. For Indian investors, drawing trendlines on indices like the Nifty 50 and Sensex can provide a broader understanding of market direction.
Moving averages (MAs) smooth out price data by calculating the average price over a specific period. They help identify trends and potential support and resistance levels. Common types include:
Popular moving average periods include 50-day, 100-day, and 200-day MAs. Crossovers of different moving averages (e.g., the 50-day MA crossing above the 200-day MA, known as a “golden cross”) can generate buy signals, while the opposite (a “death cross”) can signal a sell signal. For investors in ELSS (Equity Linked Savings Schemes) or other equity-based instruments, monitoring long-term moving averages can help assess the overall health of the market.
The RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions in the price of a stock or asset. It ranges from 0 to 100.
best technical analysis tools in trading app
Divergences between the RSI and price action can also provide valuable signals. For example, if the price is making new highs but the RSI is failing to make new highs, it could indicate a weakening trend.
The MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price. It consists of two lines: the MACD line and the signal line.
The MACD is particularly useful for identifying potential trend reversals and confirming the strength of existing trends. It’s a valuable tool for both short-term traders and long-term investors.
Fibonacci retracement levels are horizontal lines that indicate potential support and resistance levels based on Fibonacci ratios (23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%). These levels are derived from the Fibonacci sequence, a mathematical sequence found throughout nature and often observed in financial markets.
To use Fibonacci retracements, identify a significant high and low point on a chart. The retracement levels will then be drawn between these points, indicating potential areas where the price may find support or resistance. These levels can be particularly useful for setting profit targets and stop-loss orders.
Volume represents the number of shares traded during a specific period. Analyzing volume can provide valuable insights into the strength and validity of price movements.
Volume analysis can help differentiate between genuine price movements and false breakouts. Sudden spikes in volume often accompany significant price changes.
Bollinger Bands consist of a middle band (usually a 20-day SMA) and two outer bands that are a certain number of standard deviations (typically two) away from the middle band. They measure the volatility of a stock or asset.
Bollinger Bands can be used to identify potential breakout opportunities and to gauge the relative expensiveness or cheapness of a stock.
While these tools are powerful, it’s essential to remember that no single indicator is foolproof. The best approach is to combine multiple tools and techniques to confirm signals and make more informed decisions. Here are some tips for integrating technical analysis into your trading strategy:
Many Indian trading apps also offer features like screeners, which allow you to filter stocks based on specific technical criteria, making it easier to identify potential trading opportunities. Always remember to adhere to SEBI guidelines and regulations while trading in the Indian stock market.
Mastering technical analysis tools in trading apps can significantly empower Indian investors to make more informed and profitable trading decisions. By understanding chart patterns, indicators, and volume analysis, you can gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics and identify potential investment opportunities. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or a beginner, incorporating technical analysis into your trading strategy can help you navigate the complexities of the Indian stock market with greater confidence and success. Remember to continuously learn and adapt your strategies as market conditions evolve, and always prioritize risk management.


Demystifying Intraday Trading: Understand the risks, strategies, and essential tools for navigating the fast-paced Indian stock market. Learn how to potentially
Demystifying intraday trading: Understand the risks, strategies, and essential tools for navigating the fast-paced Indian stock market. Learn how to potentially profit from daily price movements on the NSE & BSE.
The Indian stock market, with its vibrant energy and potential for quick returns, attracts investors from all walks of life. Among the various trading styles, one that stands out for its rapid-fire nature and potential for high gains (and equally high risks) is intraday trading. But what exactly is it, and is it the right fit for you? This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of intraday trading in the Indian context, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions.
Unlike long-term investments like mutual funds or systematic investment plans (SIPs), which focus on wealth creation over extended periods, or even medium-term strategies where you might hold equity for a few months or years, intraday trading is a short-term game. It’s about capitalizing on the small price fluctuations that occur within a single trading day. All positions are typically squared off before the market closes at 3:30 PM IST, ensuring no overnight risk.
In its simplest form, intraday trading involves buying and selling stocks within the same trading day. The objective is to profit from short-term price movements. Traders analyze market trends, news events, and technical indicators to identify opportunities to buy low and sell high (or short sell high and buy low) within the same trading session. No shares are delivered or taken possession of in this method; profit or loss is the difference between the buy and sell price.
It’s crucial to differentiate intraday trading from delivery-based trading. In delivery-based trading, you buy shares with the intention of holding them for a longer period, potentially days, weeks, months, or even years. You take delivery of the shares in your Demat account. In contrast, intraday trading is purely speculative. You’re not interested in the long-term value of the company; you’re solely focused on predicting short-term price movements. If you fail to square off the position before market closure, your broker will typically do it automatically, sometimes at a penalty.
Like any investment strategy, intraday trading comes with its own set of pros and cons. It’s essential to weigh these factors carefully before venturing into this high-risk arena.
To succeed in intraday trading, you need to equip yourself with the right tools and techniques. Here are some essential elements:
Technical analysis involves studying historical price and volume data to identify patterns and trends that can help predict future price movements. Key technical indicators include:
While primarily used for long-term investing, a basic understanding of fundamental analysis can be helpful for intraday trading. Keeping an eye on news events, company announcements, and economic data releases can provide valuable insights into potential price movements. For example, a sudden announcement regarding a key regulatory approval for a pharmaceutical company listed on the NSE could cause a significant spike in its stock price.
Risk management is paramount in intraday trading. It’s crucial to set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and to define your risk-reward ratio before entering a trade. A common strategy is to risk no more than 1-2% of your trading capital on any single trade.
Emotions can be your worst enemy in intraday trading. Fear and greed can lead to impulsive decisions and costly mistakes. Developing a disciplined approach and sticking to your trading plan is essential for success. Resist the urge to chase losses or become overly confident after a winning streak.
Selecting the right stocks is crucial for intraday trading. Look for stocks that are highly liquid, meaning they have high trading volumes, and that exhibit sufficient volatility, meaning their prices fluctuate significantly throughout the day. Stocks listed on the NSE Nifty 50 or BSE Sensex are often good candidates.
Choose a reliable and user-friendly trading platform that provides real-time market data, charting tools, and efficient order execution. Many brokers in India offer specialized platforms for intraday traders.
Numerous strategies can be employed in intraday trading. Here are a few popular ones:
Profits earned from intraday trading are generally considered speculative business income and are taxed according to your income tax slab. It’s essential to maintain accurate records of all your trades and consult with a tax advisor to understand the tax implications and claim any eligible deductions. Intraday profits are not eligible for the benefits available under investments like ELSS mutual funds, PPF, or NPS. All expenses related to trading can be claimed as business expenses, which can reduce the tax burden.
Intraday trading is not for everyone. It requires a significant investment of time, effort, and capital. Before you jump into the market, ask yourself these questions:
If you answered “no” to any of these questions, intraday trading may not be the right fit for you. Consider exploring other investment options, such as long-term equity investing, mutual funds, or debt instruments, which may be more suitable for your risk tolerance and financial goals.
If the high-pressure environment of intraday trading seems daunting, numerous alternatives offer less volatile pathways to wealth creation in the Indian financial landscape:
Intraday trading can be a potentially lucrative but also highly risky endeavor. While the allure of quick profits is strong, it’s essential to approach it with caution, knowledge, and a well-defined trading plan. Before venturing into the world of intraday trading, educate yourself thoroughly, practice with paper trading or virtual accounts, and understand the risks involved. Remember to prioritize risk management and never invest more than you can afford to lose. Consider consulting with a financial advisor to determine if intraday trading aligns with your overall financial goals and risk tolerance.
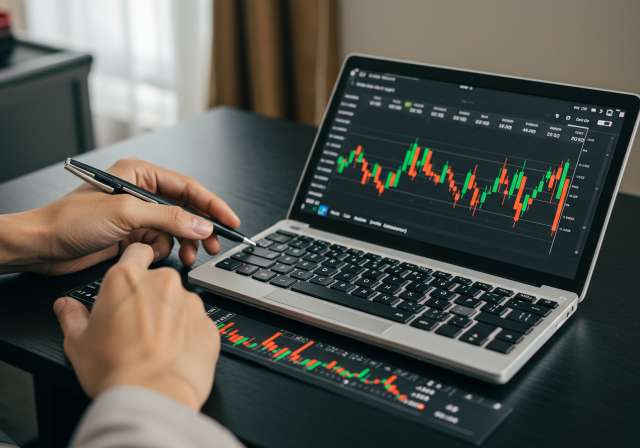


Unlock trading success! Discover the best technical analysis tools in trading app features for Indian investors. Master charts, indicators, & strategies to prof
Unlock trading success! Discover the best technical analysis tools in trading app features for Indian investors. Master charts, indicators, & strategies to profit in the Indian stock market (NSE/BSE). Maximize returns with informed decisions. Start your journey to financial independence today!
The Indian stock market, encompassing the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), offers tremendous opportunities for wealth creation. However, success in the equity markets demands more than just luck. It requires a disciplined approach, a thorough understanding of market dynamics, and the strategic application of technical analysis.
Technical analysis, in essence, is the art and science of interpreting market data, primarily price and volume, to forecast future price movements. It’s a powerful tool in the hands of informed investors, allowing them to identify potential entry and exit points, manage risk effectively, and ultimately, enhance their investment returns. This is especially relevant for the modern Indian investor who increasingly relies on trading apps for their investment activities.
In today’s fast-paced trading environment, access to sophisticated technical analysis tools through trading apps is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. These apps empower investors to conduct in-depth market research, analyze price patterns, and make informed trading decisions, all from the convenience of their smartphones.
Before diving into the specific tools, let’s understand why technical analysis is so crucial for Indian investors:
For Indian investors who are building wealth through systematic investment plans (SIPs) in mutual funds, understanding basic technical indicators can help time lump-sum investments during market corrections to achieve better returns.
Trading apps offer a plethora of technical analysis tools, but some are more essential than others. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most crucial tools for Indian investors:
Different chart types present price data in distinct ways, each offering unique insights:
Trendlines are lines drawn on a chart to connect a series of highs (downtrend) or lows (uptrend). They help to visually identify the direction of the market and can be used to anticipate potential support and resistance levels.
Support levels are price levels where buying pressure is strong enough to prevent the price from falling further. Resistance levels are price levels where selling pressure is strong enough to prevent the price from rising further. Identifying these levels can help investors anticipate potential price reversals or breakouts.
Moving averages are calculated by averaging the price of a security over a specific period. They smooth out price fluctuations and make it easier to identify the underlying trend. Common moving average periods include 50-day, 100-day, and 200-day moving averages.
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum indicator that measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions in the price of a stock or other asset. Values above 70 generally indicate overbought conditions, while values below 30 generally indicate oversold conditions.
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price. It consists of the MACD line, the signal line, and the histogram. Crossovers between the MACD line and the signal line can indicate potential buy or sell signals. Divergence between the MACD and the price action can also signal potential trend reversals.
Fibonacci retracements are horizontal lines drawn on a chart to indicate potential support and resistance levels based on Fibonacci ratios (23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 100%). These ratios are derived from the Fibonacci sequence and are believed to have predictive value in financial markets.
Volume analysis involves studying the trading volume associated with price movements. High volume during a price increase can confirm the strength of the uptrend, while high volume during a price decrease can confirm the strength of the downtrend. Divergence between price and volume can also signal potential trend reversals.
Technical analysis isn’t a standalone solution; it’s most effective when integrated with a broader investment strategy. Here’s how Indian investors can integrate these tools:
For example, an investor saving tax through Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS) funds can use technical analysis to decide when to invest a lump sum rather than using a SIP. Similarly, for those investing in the National Pension System (NPS), understanding market trends can help decide the allocation of funds between equity and debt.
Selecting the right trading app is crucial for effective technical analysis. Consider the following factors:
Technical analysis is a powerful tool that can empower Indian investors to make informed trading decisions and achieve their financial goals. By mastering the essential tools and integrating them into a well-defined investment strategy, investors can navigate the complexities of the Indian stock market with confidence and increase their chances of success. Remember to consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions. Investing in the stock market carries inherent risks and it is important to invest wisely and responsibly.
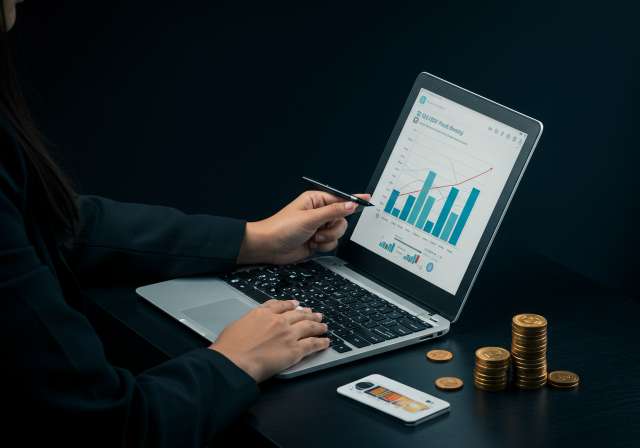


Intraday trading offers the potential for high returns, but it also carries significant risks. It is not suitable for everyone. Before venturing into intraday trading, carefully assess your risk tolerance, financial situation, and time commitment. Invest the time to learn the necessary skills, develop a robust trading strategy, and practice effective risk management. Remember to start small, manage your emotions, and stay disciplined. If you are unsure, consider seeking advice from a qualified financial advisor.
Demystifying intraday trading: Learn the risks & rewards of buying & selling stocks within the same day in the Indian stock market. Is it right for you? Understand strategies, tools & regulations for successful intraday trading.
The Indian stock market, with its dynamic fluctuations and potential for quick gains, attracts investors from all walks of life. Whether you are a seasoned professional or a novice just starting to explore investment options, the allure of participating in the growth story of India is undeniable. From long-term investments in blue-chip companies listed on the NSE and BSE to shorter-term strategies like Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs) in equity mutual funds, there’s a spectrum of opportunities available. However, among the various trading styles, one stands out for its high-octane nature and the potential for rapid profits (and losses): intraday trading. This guide aims to demystify this complex trading style, offering insights relevant to Indian investors looking to navigate its intricacies.
At its core, intraday trading, sometimes called day trading, involves buying and selling stocks or other financial instruments within the same trading day. The primary goal is to capitalize on small price movements and profit from the volatility of the market. Unlike long-term investors who hold assets for months or years, intraday traders close their positions before the market closes, avoiding overnight risks and associated charges. In India, this means squaring off all positions before the 3:30 PM deadline (for equities), as determined by the exchanges.
The primary attraction of intraday trading is the potential for high returns in a short period. Skilled traders can leverage market fluctuations to generate significant profits. However, it’s crucial to understand that this potential comes with significant risks. The market’s unpredictable nature can lead to substantial losses just as quickly as it can generate gains. In essence, successful intraday trading requires a combination of knowledge, discipline, and a well-defined strategy.
Successfully navigating the world of intraday trading requires more than just luck; it necessitates a robust set of tools and well-honed techniques. These tools help traders analyze market trends, identify potential opportunities, and manage risk effectively.
A well-defined trading strategy is the cornerstone of successful intraday trading. This strategy should outline specific criteria for selecting stocks, entering trades, setting stop-loss orders, and taking profits. However, even the best strategy is useless without effective risk management.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) plays a crucial role in regulating the Indian stock market and protecting investors. Intraday traders must be aware of and comply with SEBI’s guidelines and regulations. These regulations aim to ensure fair trading practices, prevent market manipulation, and promote investor confidence.
It is essential to choose a SEBI-registered broker and ensure that they comply with all applicable regulations. Familiarize yourself with SEBI’s investor protection guidelines and take steps to protect your interests.
Profits generated from intraday trading are considered speculative business income and are taxed according to the applicable income tax slab rates. It is essential to maintain accurate records of all your trades and consult with a tax advisor to ensure compliance with tax laws.
Seek professional tax advice to understand the tax implications of intraday trading and ensure compliance with all applicable laws.
Before diving into intraday trading, it’s crucial to consider alternative investment options and assess their suitability based on your risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. Compared to less risky investments such as Public Provident Fund (PPF) or National Pension System (NPS), intraday trading is considerably higher risk. Similarly, even compared to SIP investments in Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS) which come with a lock-in period but offer tax benefits, intraday trading is far more volatile.
Understanding the risk-return profile of different investment options will help you make informed decisions and diversify your portfolio effectively. Intraday trading should be considered as a small part of a well-diversified investment strategy, rather than the sole focus.


Unlock your trading potential with a powerful trading app! Navigate the Indian stock market with ease, access real-time data, and execute trades seamlessly. Dis
Unlock your trading potential with a powerful trading app! Navigate the Indian stock market with ease, access real-time data, and execute trades seamlessly. Discover the features you need for successful investing on the NSE & BSE.
The Indian financial landscape is rapidly evolving, with a significant shift towards digital platforms. More and more investors, from seasoned professionals to first-time entrants, are turning to mobile trading apps to manage their portfolios and participate in the equity markets. This surge in popularity is fueled by convenience, accessibility, and the availability of real-time market data at your fingertips. Gone are the days of relying solely on brokers and physical trading floors. Today, a smartphone and a reliable internet connection are all you need to potentially build wealth.
For Indian investors, understanding the nuances of the NSE (National Stock Exchange) and BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange) is paramount. A well-designed trading app can be your trusted companion, providing the tools and information necessary to make informed investment decisions. However, with a plethora of options available in the market, choosing the right app can feel overwhelming. This article will guide you through the key factors to consider when selecting a trading app that aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Before diving into specific apps, let’s explore the essential features that define a robust and user-friendly trading platform:
A clean, intuitive interface is crucial for efficient trading. The app should be easy to navigate, with clear displays of market data, order placement options, and portfolio summaries. Look for apps that offer customizable watchlists, allowing you to track your favorite stocks and indices in real-time.
Access to accurate and up-to-date market data is non-negotiable. The app should provide real-time quotes, historical charts, and technical indicators to help you analyze price trends and identify potential trading opportunities. Consider apps that offer advanced charting tools, such as Fibonacci retracements and moving averages.
Flexibility in order placement is essential for managing risk and executing trades effectively. The app should support various order types, including:
A good trading app should offer research and analysis tools to help you make informed investment decisions. This may include:
Seamless fund transfer and withdrawal options are essential for managing your capital. The app should support various payment methods, including UPI, net banking, and debit/credit cards. Check the processing times and associated fees for fund transfers and withdrawals.
Security is paramount when dealing with your finances. Ensure the app employs robust security measures, such as two-factor authentication and data encryption, to protect your account from unauthorized access. A reliable app with minimal downtime is also crucial for executing trades efficiently.
Responsive and helpful customer support is essential in case you encounter any issues or have questions about the app. Look for apps that offer multiple channels for support, such as phone, email, and chat.
Understand the commission structure and other fees associated with using the app. Some apps offer flat-fee pricing, while others charge a percentage of the trade value. Consider your trading frequency and average trade size to determine the most cost-effective option.
While equity trading is a popular choice, consider exploring other investment options available through the app, such as:
Mutual funds offer a diversified way to invest in the market. Look for apps that allow you to invest in a wide range of mutual funds, including equity funds, debt funds, and hybrid funds. Consider investing through Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs) for long-term wealth creation.
Participate in IPOs to invest in newly listed companies. The app should provide information about upcoming IPOs and allow you to apply directly through the platform.
Invest in gold in a dematerialized form through SGBs. These bonds offer a fixed interest rate and are backed by the government of India.
Plan for your retirement with the NPS, a government-sponsored pension scheme. The app should allow you to open and manage your NPS account.
Access fixed deposits and bonds offered by various banks and financial institutions through the app.
It’s crucial to choose a trading app that is regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). SEBI is the regulatory authority responsible for overseeing the Indian securities market and protecting the interests of investors. Trading apps that comply with SEBI regulations adhere to strict standards of transparency, security, and investor protection.
Once you’ve chosen a trading app, here are some tips for successful mobile trading:
In conclusion, selecting the right trading app is a crucial step towards empowering your financial journey in the Indian stock market. By carefully considering the factors outlined in this article, you can choose a platform that aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance. Remember to prioritize security, reliability, and user-friendliness. A well-chosen app, combined with a disciplined approach to trading, can help you achieve your financial aspirations. The market offers avenues to invest in Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS) and Public Provident Fund (PPF) too, which can be tracked separately on your demat accounts opened through the apps. Leverage the power of technology and embark on your path to financial success!


Unlock trading success! Discover the best technical analysis tools in trading apps for Indian investors. From candlestick patterns to RSI, empower your investme
Unlock trading success! Discover the best technical analysis tools in trading apps for Indian investors. From candlestick patterns to RSI, empower your investment decisions and maximize returns. Start smart trading today!
The Indian stock market, encompassing exchanges like the NSE (National Stock Exchange) and BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange), offers immense opportunities for wealth creation. However, successful trading requires more than just intuition. It demands a disciplined approach rooted in sound analysis. Technical analysis, the art of interpreting market data to predict future price movements, is a cornerstone of such a strategy. And in today’s fast-paced world, having access to powerful technical analysis tools within your trading app is crucial for staying ahead of the curve.
For Indian investors, from seasoned traders to those just starting their journey with SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans) and ELSS (Equity Linked Savings Schemes) mutual funds, understanding and utilizing these tools can significantly improve their investment outcomes. Whether you are saving for retirement through NPS (National Pension System) or building a long-term portfolio, incorporating technical analysis can help you make informed decisions and mitigate risks.
Technical analysis provides a framework for understanding market psychology and identifying potential trading opportunities. Here’s why it’s so valuable, particularly for Indian traders:
Modern trading apps are packed with a plethora of technical analysis tools. Here are some of the most important ones that every Indian trader should be familiar with:
Candlestick charts are a visual representation of price movements over a specific period. Each candlestick represents a single trading period and displays the open, high, low, and close prices. By analyzing candlestick patterns, traders can identify potential trend reversals and continuations. Popular candlestick patterns include:
Moving averages (MAs) are used to smooth out price fluctuations and identify the underlying trend. They are calculated by averaging the price over a specified period. Common types of moving averages include:
Traders often use moving averages to identify support and resistance levels and to generate buy and sell signals. Crossovers between different moving averages (e.g., a 50-day MA crossing above a 200-day MA) are often interpreted as bullish signals.
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum indicator that measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions in the market. It ranges from 0 to 100. Typically, an RSI reading above 70 indicates an overbought condition, while a reading below 30 indicates an oversold condition. Traders use the RSI to identify potential trend reversals and to confirm other technical signals.
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price. It consists of the MACD line, the signal line, and the histogram. Traders use the MACD to identify potential buy and sell signals, as well as to spot divergences between price and momentum, which can indicate potential trend reversals.
Fibonacci retracements are horizontal lines that indicate potential support and resistance levels based on Fibonacci ratios. These ratios are derived from the Fibonacci sequence (0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, etc.). Common Fibonacci retracement levels include 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%, and 78.6%. Traders use Fibonacci retracements to identify potential entry and exit points for their trades.
Volume represents the number of shares or contracts traded during a specific period. Analyzing volume can provide valuable insights into the strength of a trend. Rising prices accompanied by increasing volume suggest a strong bullish trend, while falling prices accompanied by increasing volume suggest a strong bearish trend. Low volume can indicate a weak trend or a potential reversal.
Support and resistance levels are key price points where the price is likely to find support (i.e., bounce upwards) or resistance (i.e., encounter selling pressure). These levels can be identified by analyzing historical price data and looking for areas where the price has repeatedly reversed its direction. Traders use support and resistance levels to identify potential entry and exit points and to set stop-loss orders.
Not all trading apps are created equal. When choosing a trading app for technical analysis, consider the following factors:
While technical analysis is a powerful tool, it’s important to remember that it’s just one piece of the puzzle. Successful traders often combine technical analysis with other investment strategies, such as fundamental analysis and risk management. For example, you might use fundamental analysis to identify undervalued companies and then use technical analysis to time your entry and exit points. You might also use technical analysis to set stop-loss orders and manage your risk effectively.
Let’s look at some hypothetical examples of how technical analysis can be used to trade Indian stocks:
No matter how sophisticated your technical analysis skills are, it’s important to remember that trading always involves risk. Before investing in the stock market, it’s crucial to understand your risk tolerance and to set appropriate stop-loss orders to protect your capital. Never invest more than you can afford to lose. Diversification across different asset classes is also a crucial part of risk management. Consider investing in instruments like PPF (Public Provident Fund) or gold alongside your equity investments.
Technical analysis is an invaluable tool for Indian traders looking to navigate the complexities of the stock market. By understanding and utilizing the various technical indicators available in trading apps, you can make more informed trading decisions, manage risk effectively, and ultimately improve your investment outcomes. The best technical analysis tools in trading app are the ones you understand and apply consistently as part of a wider trading plan. Remember to always combine technical analysis with other investment strategies and to manage your risk prudently. Happy trading!
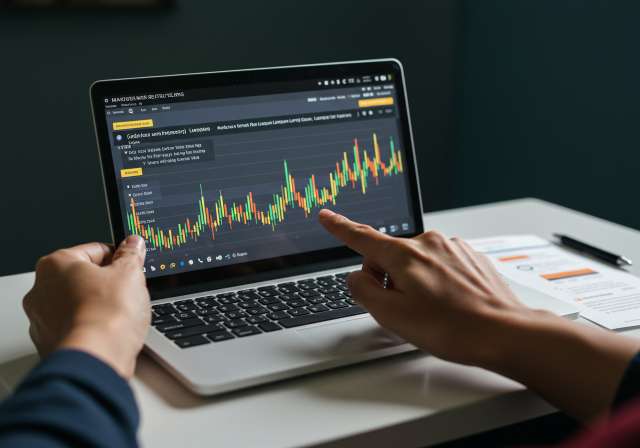

If you’re new to the stock market, it’s generally advisable to start with long-term investing or SIPs before venturing into the more volatile world of intraday trading. Consider starting with paper trading (simulated trading) to gain experience and test your strategies without risking real money. Learning about different asset classes like fixed deposits, gold, and real estate can also help create a more well-rounded portfolio.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) plays a crucial role in regulating the Indian stock market and protecting investors. SEBI sets rules and regulations for brokers, trading platforms, and market participants to ensure fair and transparent trading practices. Investors should only trade with SEBI-registered brokers to ensure that their interests are protected.
Intraday trading can be a rewarding endeavor, but it’s crucial to approach it with caution, discipline, and a thorough understanding of the risks involved. It’s not a get-rich-quick scheme; it requires dedication, continuous learning, and a well-defined trading strategy. By educating yourself, managing your risks effectively, and staying disciplined, you can increase your chances of success in the dynamic world of intraday trading in the Indian stock market. Remember to always consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
Demystifying intraday trading: Learn about strategies, risks, and tips for navigating the Indian stock market. Is it right for you? Understand the pros and cons of intraday trading in India.
The Indian stock market, with the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and National Stock Exchange (NSE) at its core, offers a multitude of opportunities for investors. Among them, intraday trading stands out as a fast-paced, high-stakes game. But what exactly is it, and is it the right fit for you? This guide aims to demystify intraday trading, providing a comprehensive overview for beginners eager to understand its nuances within the Indian financial landscape.
Unlike traditional investing, where you buy and hold stocks for the long term, intraday trading involves buying and selling stocks within the same trading day. The goal is to profit from small price fluctuations that occur throughout the day. All positions are squared off before the market closes, meaning you don’t hold any stocks overnight. It’s a strategy centered around short-term price predictions and leveraging market volatility.
Before diving into the specifics, it’s crucial to understand some fundamental concepts:
Let’s break down how intraday trading works in the Indian context:
Success in intraday trading requires a well-defined strategy and disciplined execution. Here are some popular strategies:
This strategy involves identifying and following the prevailing trend in the market. If the market is trending upward, you’d look to buy stocks; if it’s trending downward, you’d consider short selling. Technical indicators like moving averages and trendlines can help identify trends.
Breakout trading involves identifying key support and resistance levels. When a stock price breaks through these levels, it can signal a potential trend reversal or continuation. Traders often look for increased volume accompanying the breakout to confirm the signal.
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy that aims to profit from small price movements. Scalpers typically hold positions for very short periods, often just a few seconds or minutes, and aim to accumulate small profits on each trade.
This strategy involves identifying stocks that are trading within a defined price range. Traders buy at the lower end of the range and sell at the upper end, capitalizing on the predictable price fluctuations.
Risk management is paramount in intraday trading. Here’s how to mitigate potential losses:
It’s important to understand how intraday trading differs from other investment options available in India:
Each of these options has different risk-return profiles and caters to different investment goals. Intraday trading, with its high risk and potential for high rewards, is best suited for experienced traders with a strong understanding of the market.
A significant part of succeeding at intraday trading is mastering your emotions. Fear and greed are the biggest enemies of a trader. Here’s how to manage your psychological state:
Having the right tools at your disposal can significantly enhance your trading performance:
Intraday trading is not for everyone. It requires a significant time commitment, a high level of discipline, and a strong understanding of the market. Consider the following factors before venturing into intraday trading: